Plasmids
pOpt_cCA_mVenus_Paro
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the mVenus (YFP variant) reporter expression cassette (with N-terminal cCA secretion signal) and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is paromomycin resistance aphVIII (Sizova et al. 2001).
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_cCA_mCerulean3_Paro
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the mCerulean3 (a CFP variant) reporter expression cassette (with N-terminal cCA secretion signal) and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is paromomycin resistance aphVIII (Sizova et al. 2001).
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_cCA_gLuc_Paro
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the gLuc (Gaussia princeps luciferase) reporter expression cassette (with N-terminal cCA secretion signal) and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is paromomycin resistance aphVIII (Sizova et al. 2001).
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_cCA_Clover_Paro
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the Clover (a GFP variant) reporter expression cassette (with N-terminal cCA secretion signal) and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is paromomycin resistance aphVIII (Sizova et al. 2001).
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_cCA_mRuby2_Paro
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the mRuby2 (RFP variant) reporter expression cassette (with N-terminal cCA secretion signal) and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is paromomycin resistance aphVIII (Sizova et al. 2001).
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_mVenus_Hyg
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
NCBI accession number: KM061065
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the mVenus (YFP variant) reporter expression cassette and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is hygromycin B resistance aphVII.
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_mCerulean3_Hyg
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
NCBI accession number: KM061066
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the mCerulean3 (a CFP variant) reporter expression cassette and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is hygromycin B resistance aphVII.
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_gLuc_Hyg
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
NCBI accession number: KM061064
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the gLuc (Gaussia princeps luciferase) reporter expression cassette and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is hygromycin B resistance aphVII.
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_mRuby2_Hyg
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
NCBI accession number: KM061068
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the mRuby2 (RFP variant) reporter expression cassette and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is hygromycin B resistance aphVII.
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_Clover_Hyg
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
NCBI accession number: KM061067
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the Clover (a GFP variant) reporter expression cassette and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is hygromycin B resistance aphVII.
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_cCA_mVenus_Hyg
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert pOptimized template vector containing the mVenus (YFP variant) reporter expression cassette (with N-terminal cCA secretion signal) and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is hygromycin B resistance aphVII.
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_cCA_mCerulean3_Hyg
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert pOptimized template vector containing the mCerulean3 (a CFP variant) reporter expression cassette (with N-terminal cCA secretion signal) and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is hygromycin B resistance aphVII.
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_cCA_gLuc_Hyg
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert pOptimized template vector containing the gLuc (Gaussia princeps luciferase) reporter expression cassette (with N-terminal cCA secretion signal) and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is hygromycin B resistance aphVII.
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_cCA_mRuby2_Hyg
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert pOptimized template vector containing the mRuby2 (RFP variant) reporter expression cassette (with N-terminal cCA secretion signal) and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is hygromycin B resistance aphVII.
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_cCA_Clover_Hyg
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert pOptimized template vector containing the Clover (a GFP variant) reporter expression cassette (with N-terminal cCA secretion signal) and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is hygromycin B resistance aphVII.
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pET24a(+)_mCerulean3
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, September 2014
NCBI accession number: KM504958
The pOpt system was originally built with four fluorescent protein standards and one luciferase.
The Gaussia princeps luciferase is available as a secreted product standard from Avidity: https://www.avidity.com.
However, the four fluorescent reporters, mCerulean3 (a bright cyan FP variant), mVenus (a bright yellow FP variant), Clover (a very bright green FP variant), and mRuby2 (a bright red FP variant from Entacmaea quadricolor), are not commercially available as protein standards.
Since the pOptimized expression system contains two introns (1 and 2 of RBCS2), it would require specialized reconstruction of the genes without introns for the researcher to make Escherichia coli expression constructs to use as standards.
We, therefore, created E. coli codon optimized versions of the four fluorescent reporters containing the extra amino acids on C- and N-termini that are a product of the pOpt restriction sites, and included the StrepII tag on their C-terminus as is also found in the pOpt reporters. The protein products from these E. coli expression cassettes are identical to those produced from their pOpt citosolic localized counterparts.
The E. coli expression constructs are housed in the pET24a(+) backbone, driven by the T7 promoter, and are therefore inducible by addition of IPTG.
pET24a(+) is Kanamycin resistant.
The cell lines are E. coli KRX, which are designed for high recombinant protein expression purposes.
These cell lines and plasmids are usable directly without any additional cloning in standard E. coli fermentations and StrepII affinity chromatography.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pET24a(+)_mVenus
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, September 2014
NCBI accession number: KM504960
The pOpt system was originally built with four fluorescent protein standards and one luciferase.
The Gaussia princeps luciferase is available as a secreted product standard from Avidity: https://www.avidity.com.
However, the four fluorescent reporters, mCerulean3 (a bright cyan FP variant), mVenus (a bright yellow FP variant), Clover (a very bright green FP variant), and mRuby2 (a bright red FP variant from Entacmaea quadricolor), are not commercially available as protein standards.
Since the pOptimized expression system contains two introns (1 and 2 of RBCS2), it would require specialized reconstruction of the genes without introns for the researcher to make Escherichia coli expression constructs to use as standards.
We, therefore, created E. coli codon optimized versions of the four fluorescent reporters containing the extra amino acids on C- and N-termini that are a product of the pOpt restriction sites, and included the StrepII tag on their C-terminus as is also found in the pOpt reporters. The protein products from these E. coli expression cassettes are identical to those produced from their pOpt citosolic localized counterparts.
The E. coli expression constructs are housed in the pET24a(+) backbone, driven by the T7 promoter, and are therefore inducible by addition of IPTG.
pET24a(+) is Kanamycin resistant.
The cell lines are E. coli KRX, which are designed for high recombinant protein expression purposes.
These cell lines and plasmids are usable directly without any additional cloning in standard E. coli fermentations and StrepII affinity chromatography.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9.
pET24a(+)_Clover
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, September 2014
NCBI accession number: KM504959
The pOpt system was originally built with four fluorescent protein standards and one luciferase.
The Gaussia princeps luciferase is available as a secreted product standard from Avidity: https://www.avidity.com.
However, the four fluorescent reporters, mCerulean3 (a bright cyan FP variant), mVenus (a bright yellow FP variant), Clover (a very bright green FP variant), and mRuby2 (a bright red FP variant from Entacmaea quadricolor), are not commercially available as protein standards.
Since the pOptimized expression system contains two introns (1 and 2 of RBCS2), it would require specialized reconstruction of the genes without introns for the researcher to make Escherichia coli expression constructs to use as standards.
We, therefore, created E. coli codon optimized versions of the four fluorescent reporters containing the extra amino acids on C- and N-termini that are a product of the pOpt restriction sites, and included the StrepII tag on their C-terminus as is also found in the pOpt reporters. The protein products from these E. coli expression cassettes are identical to those produced from their pOpt citosolic localized counterparts.
The E. coli expression constructs are housed in the pET24a(+) backbone, driven by the T7 promoter, and are therefore inducible by addition of IPTG.
pET24a(+) is Kanamycin resistant.
The cell lines are E. coli KRX, which are designed for high recombinant protein expression purposes.
These cell lines and plasmids are usable directly without any additional cloning in standard E. coli fermentations and StrepII affinity chromatography.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pET24a(+)_mRuby2
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, September 2014
NCBI accession number: KM504961
The pOpt system was originally built with four fluorescent protein standards and one luciferase.
The Gaussia princeps luciferase is available as a secreted product standard from Avidity: https://www.avidity.com.
However, the four fluorescent reporters, mCerulean3 (a bright cyan FP variant), mVenus (a bright yellow FP variant), Clover (a very bright green FP variant), and mRuby2 (a bright red FP variant from Entacmaea quadricolor), are not commercially available as protein standards.
Since the pOptimized expression system contains two introns (1 and 2 of RBCS2), it would require specialized reconstruction of the genes without introns for the researcher to make Escherichia coli expression constructs to use as standards.
We, therefore, created E. coli codon optimized versions of the four fluorescent reporters containing the extra amino acids on C- and N-termini that are a product of the pOpt restriction sites, and included the StrepII tag on their C-terminus as is also found in the pOpt reporters. The protein products from these E. coli expression cassettes are identical to those produced from their pOpt citosolic localized counterparts.
The E. coli expression constructs are housed in the pET24a(+) backbone, driven by the T7 promoter, and are therefore inducible by addition of IPTG.
pET24a(+) is Kanamycin resistant.
The cell lines are E. coli KRX, which are designed for high recombinant protein expression purposes.
These cell lines and plasmids are usable directly without any additional cloning in standard E. coli fermentations and StrepII affinity chromatography.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pJD67
$30.00
$30.00
From Munevver Aksoy, Grossman lab, Stanford, July 2014
This plasmid contains the argininosuccinate lyase gene (encoded by ARG7) and can rescue arg2 and some other arg7 mutants.
Debuchy R, Purton S, Rochaix JD (1989) The argininosuccinate lyase gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: an important tool for nuclear transformation and for correlating the genetic and molecular maps of the ARG7 locus. EMBO J 8:2803-2809 Shimogawara K, Fujiwara S, Grossman A, Usuda H (1998) High-efficiency transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by electroporation. Genetics 148:1821-8
pASapI
$30.00
$30.00
From Saul Purton, University College London, August 2014
Chloroplast DNA sequence containing psbH-trnE2 region with an ‘expression cassette’ engineered into the intergenic MluI site. Cassette comprises of the atpA promoter/5’UTR and rbcL 3’UTR regions separated by a multiple cloning site. Note: the SapI site in the MCS is designed to allow a perfect translational fusion at the ATG of the gene-of-interest.
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
Economou C, Wannathong T, Szaub J, Purton S (2014). A simple, low cost method for chloroplast transformation of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. In: Chloroplast Biotechnology (volume editor: Pal Maliga). Methods in Molecular Biology 1132: 401-411
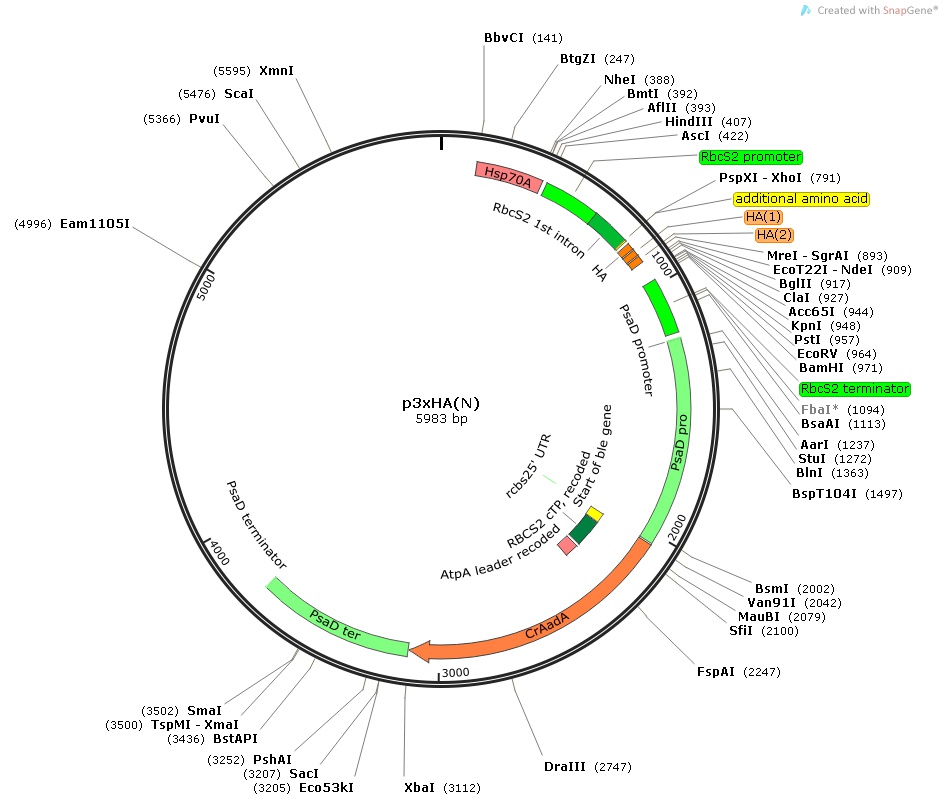
p3xHA(N)
$30.00
$30.00
From Tomohito Yamasaki, Kochi University of Technology, January 2015
Insert:
hsp70Apro::rbcS2pro::rbcS2 1st intron::3xHA epitope tag::MCS::rbcS2ter::psaDpro::codon optimized aadA::psaDter
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
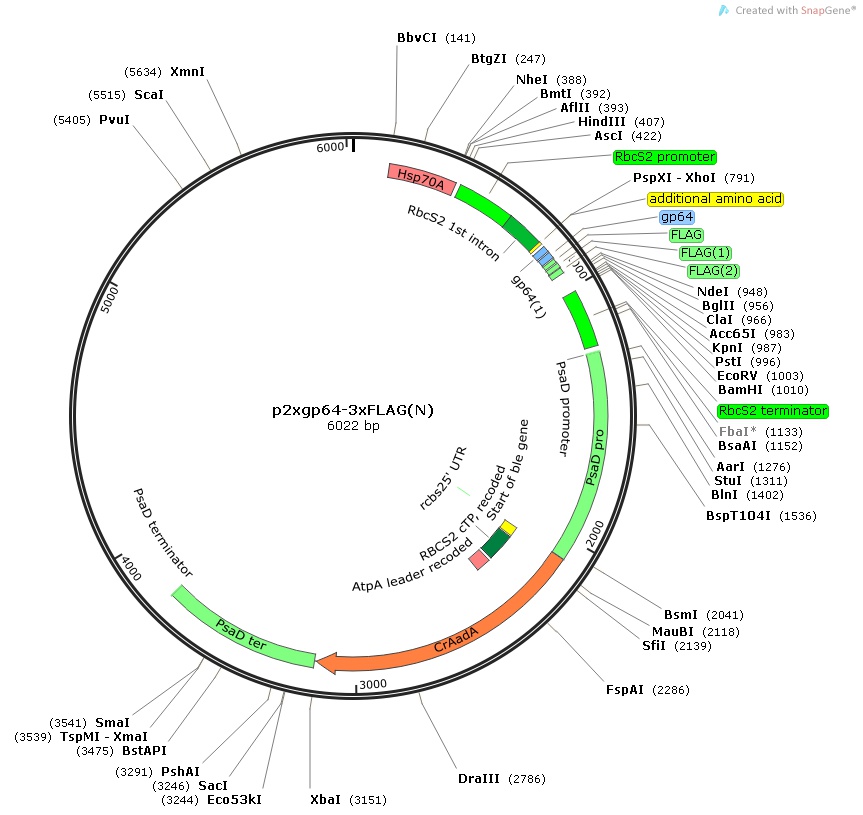
p2xgp64-3xFLAG(N)
$30.00
$30.00
From Tomohito Yamasaki, Kochi University of Technology, January 2015
Insert:
hsp70Apro::rbcS2pro::rbcS2 1st intron::2xgp64-3xFLAG epitope tag::MCS::rbcS2ter::psaDpro::codon optimized aadA::psaDter
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
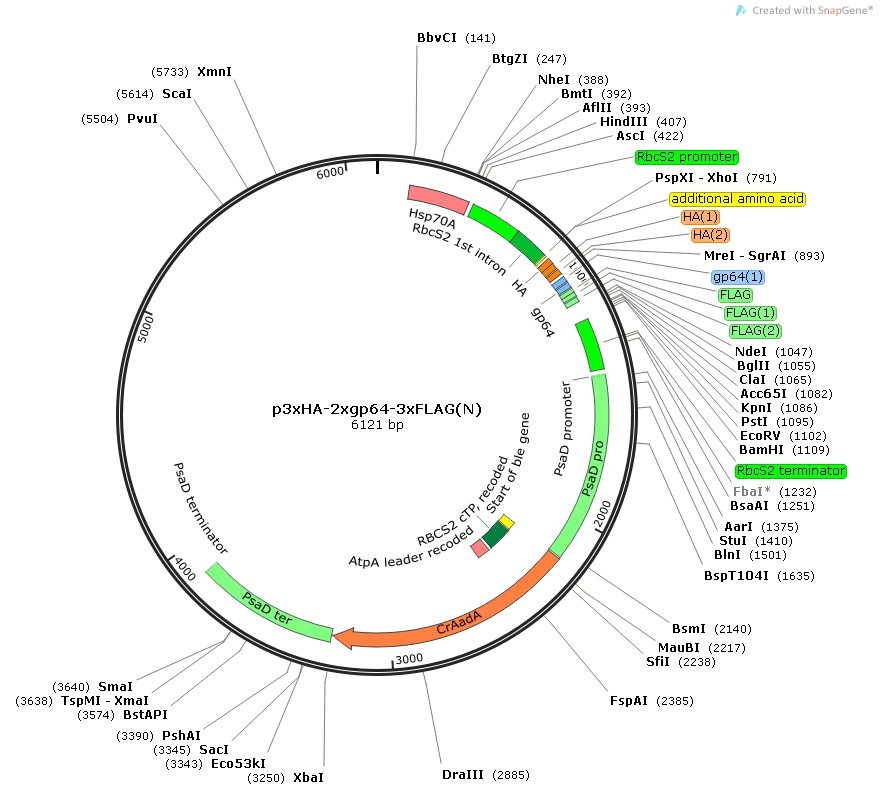
p3xHA-2xgp64-3xFLAG(N)
$30.00
$30.00
From Tomohito Yamasaki, Kochi University of Technology, January 2015
Insert:
hsp70Apro::rbcS2pro::rbcS2 1st intron::3xHA-2xgp64-3xFLAG epitope tag::MCS::rbcS2ter::psaDpro::codon optimized aadA::psaDter
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
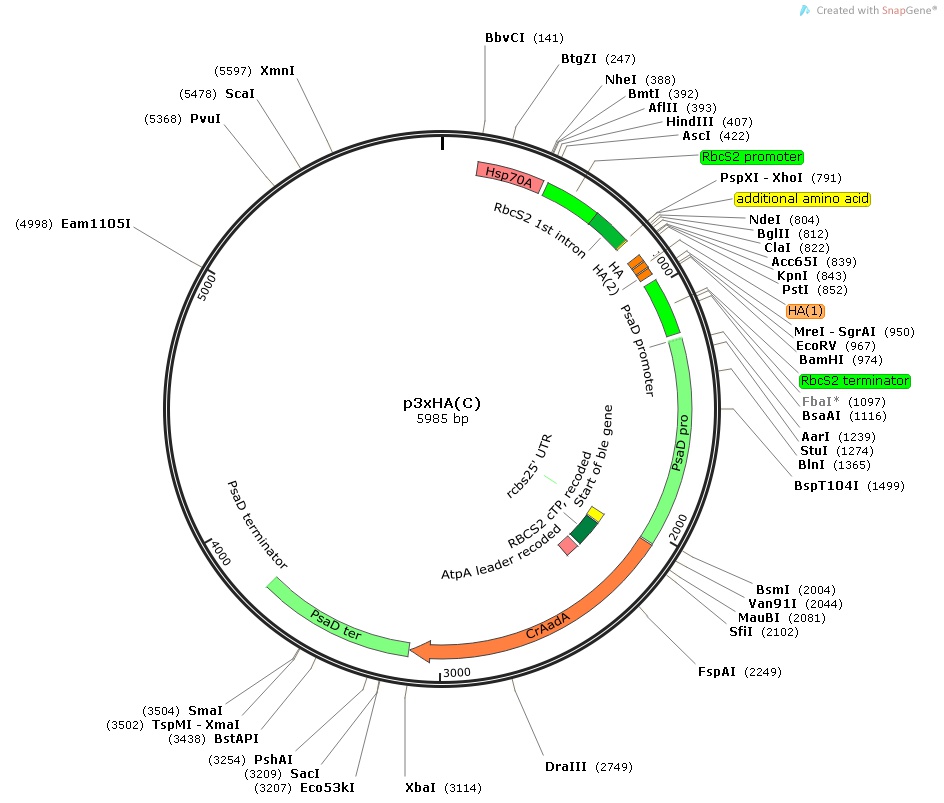
p3xHA(C)
$30.00
$30.00
From Tomohito Yamasaki, Kochi University of Technology, January 2015
Insert:
hsp70Apro::rbcS2pro::rbcS2 1st intron:: MCS:: 3xHA epitope tag::rbcS2ter::psaDpro::codon optimized aadA::psaDter
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
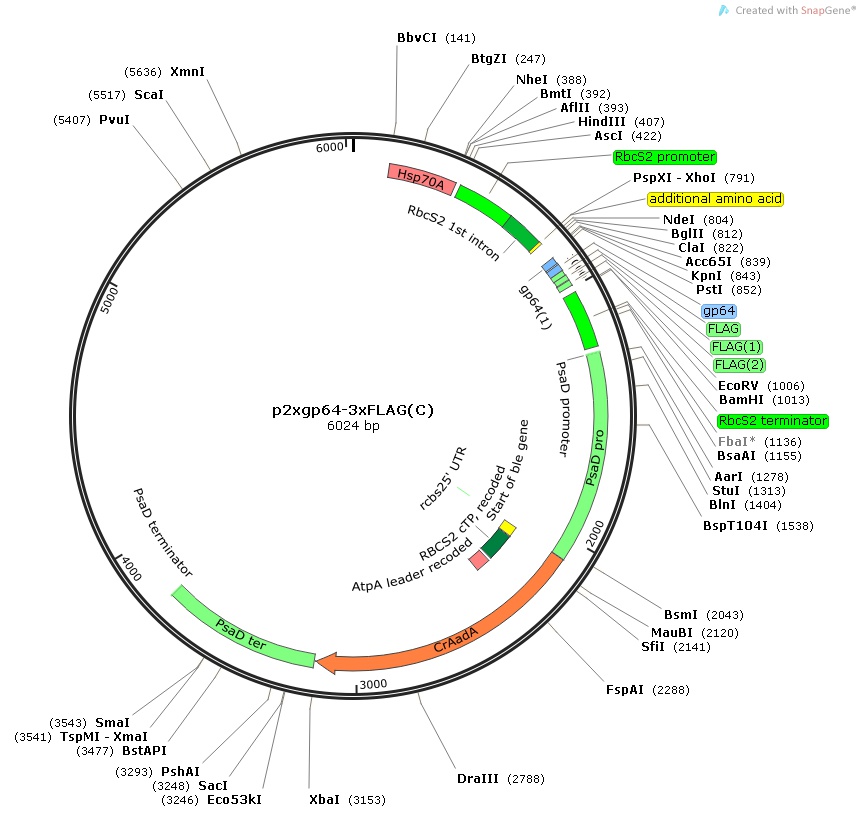
p2xgp64-3xFLAG(C)
$30.00
$30.00
From Tomohito Yamasaki, Kochi University of Technology, January 2015
Insert:
hsp70Apro::rbcS2pro::rbcS2 1st intron:: MCS:: 2xgp64-3xFLAG epitope tag::rbcS2ter::psaDpro::codon optimized aadA::psaDter
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
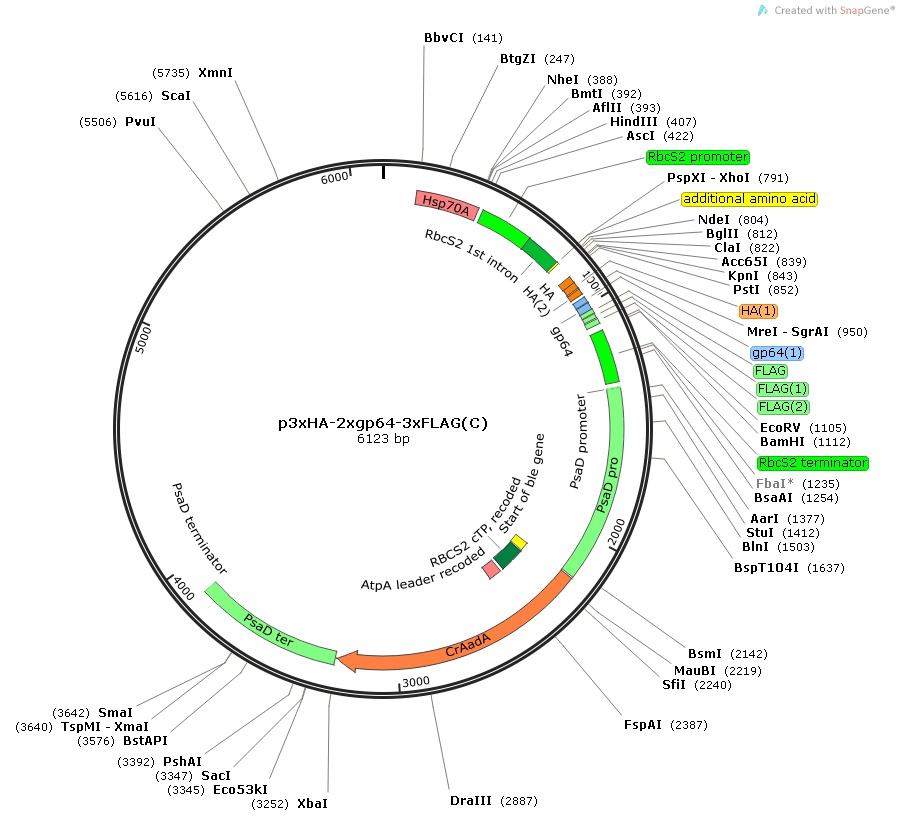
p3xHA-2xgp64-3xFLAG(C)
$30.00
$30.00
From Tomohito Yamasaki, Kochi University of Technology, January 2015
Insert:
hsp70Apro::rbcS2pro::rbcS2 1st intron:: MCS:: 3xHA-2xgp64-3xFLAG epitope tag::rbcS2ter::psaDpro::codon optimized aadA::psaDter
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
pBR9 tagBFP
$30.00
$30.00
From Beatriz Cruz, Stephen Mayfield Lab, University California-San Diego, February 2015
host strain: DH10
amp resistant
Rasala BA, Barrera DJ, Ng J, Plucinak TM, Rosenberg JN, Weeks DP, Oyler GA, Peterson TC, Haerizadeh F, Mayfield SP (2013) Expanding the spectral palette of fluorescent proteins for the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J 74:545-56
pBR9 mCerulean
$30.00
$30.00
From Beatriz Cruz, Stephen Mayfield Lab, University California-San Diego, February 2015
host strain: DH10
amp resistant
Rasala BA, Barrera DJ, Ng J, Plucinak TM, Rosenberg JN, Weeks DP, Oyler GA, Peterson TC, Haerizadeh F, Mayfield SP (2013) Expanding the spectral palette of fluorescent proteins for the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J 74:545-56
pBR9 GFP
$30.00
$30.00
From Beatriz Cruz, Stephen Mayfield Lab, University California-San Diego, February 2015
host strain: DH10
amp resistant
Rasala BA, Barrera DJ, Ng J, Plucinak TM, Rosenberg JN, Weeks DP, Oyler GA, Peterson TC, Haerizadeh F, Mayfield SP (2013) Expanding the spectral palette of fluorescent proteins for the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J 74:545-56
- «Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- …
- 15
- Next Page»